| 14. 87. 2. Creating a BoxLayout |
|
|
BoxLayout has a single constructor: |
public BoxLayout(Container target, int axis) |
|
public BoxLayout(Container target, int axis)
|
|
- The first argument is the container
- The second is the layout direction.
|
Valid directions are |
- BoxLayout.X_AXIS for a left-to-right layout and
- BoxLayout.Y_AXIS for a top-to-bottom layout.
|
A BoxLayout and container are bound together in two directions, |
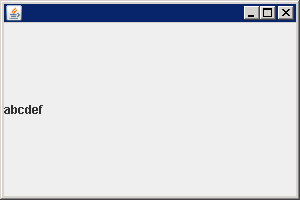
|
import java.awt.LayoutManager;
import javax.swing.BoxLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
public class BoxLayoutDemo {
public static void main(String[] a) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
LayoutManager layout = new BoxLayout(panel, BoxLayout.X_AXIS);
panel.setLayout(layout);
panel.add(new JLabel("a"));
panel.add(new JLabel("b"));
panel.add(new JLabel("c"));
panel.add(new JLabel("d"));
panel.add(new JLabel("e"));
panel.add(new JLabel("f"));
frame.add(panel);
frame.setSize(300, 200);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
|
|